This is the year of the percentages. From 99 to 47. Earlier this week, Mother Jones revealed via a secretly recorded dinner Mitt Romney as claiming that he doesn’t care about the 47% of people who do not pay income tax. He probably meant that he doesn’t care about getting their vote rather than caring for them as people, but regardless of his intention his statement did not sound good. This 47% are people who are dependent on government, or as Romney’s vice presidential candidate would say, they are “takers”. But is this true?
The great thing about news stories and infographics is that as time progresses, one has more opportunities to find data to back stories and arguments. The day of the breaking news, CNN published this simple pie donut chart. Crude, but given the breaking news it is effective.
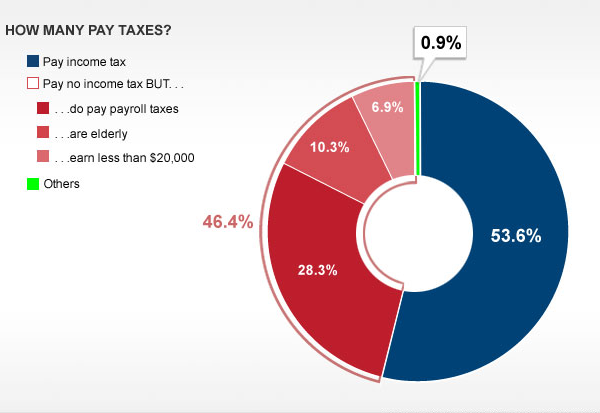
It proves that Romney was correct, that 47% of people do not pay income taxes. But, it also proves that Romney was at best glossing over the details or at worst manipulating the people listening into thinking that 47% of people do not pay taxes. It may be only 0.9% of Americans who do not pay any taxes. Furthermore, retirees and young people often do not earn income with which to pay taxes. If retired senior citizens are “takers”, I suppose Romney does not want the elderly vote so often important to the Republican base.
But news stories evolve and more statistics become available. A few days later, the New York Times published a longer infographic piece, with below a cropping of the overall.
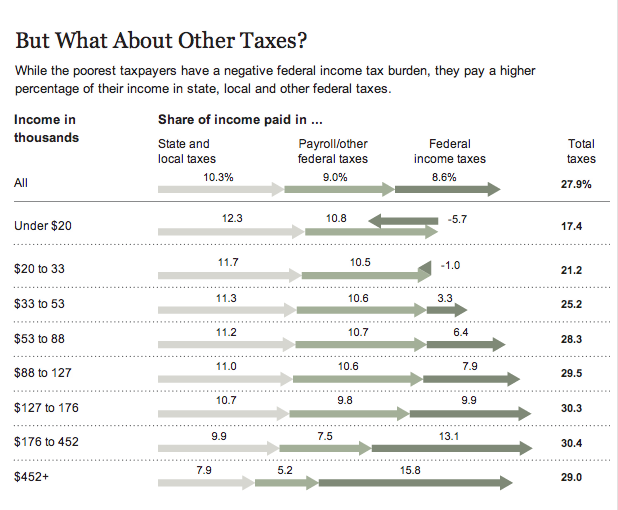
It expands upon the nature of the story and breaks down the actual tax burden of the American public. It is far more nuanced that Romney stated back in May (the original recording of the video). The poorest Americans do not pay federal income taxes, they have the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) that is designed to deal with poverty, especially amongst families with children. It is, very simply, what one would call a tax credit incentivising work. The poorest Americans, however, still must pay payroll taxes and then state and local taxes. In percentage terms, the poorest Americans pay more to their states and local governments than do the wealthiest Americans, who in turn have the greater burden at the federal level. It is worth noting that many government programmes, local schools for example, are often funded at the state and local level.
The problem with Mitt Romney’s argument on taxes is that he wants to cut taxes at the highest income brackets and cut the social safety net programmes for the lowest brackets. We already have evidence that such policies do not correlate with economic growth. They instead correlate to a worsening gap between the wealthy and the poor. Think the 1920s rather than the 1950s, 60s, and 70s.
Tax policy is worth discussing. It is worth debating. But we should do so on the facts. I cannot recall the politician who spoke these words, but as someone once said, “you are entitled to your own opinion. You are not entitled to your own facts.”
Credit for the pieces go to Susie Poppick (CNN) and the New York Times.