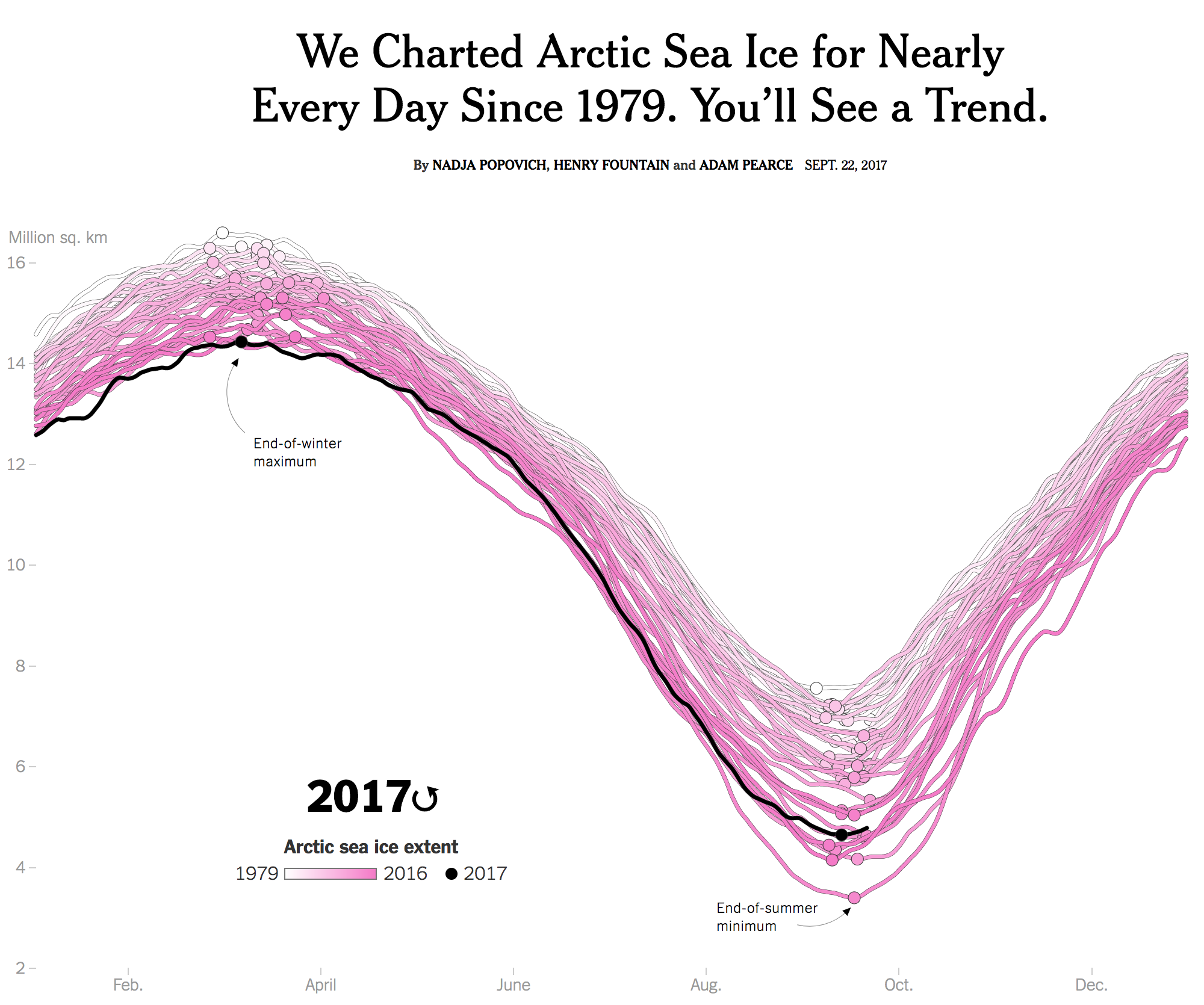
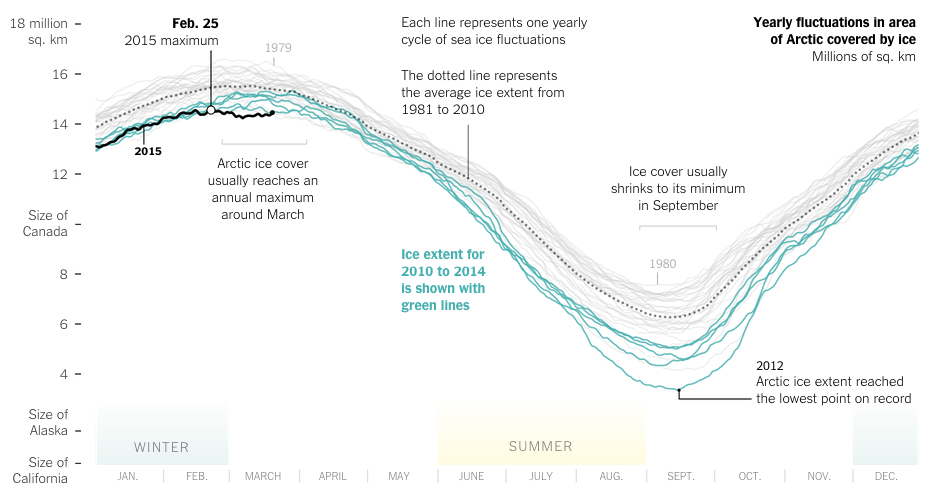
The Arctic air mass that has frozen the Midwest continues to spread and so today will be a tad chilly in Philadelphia. Yesterday, however, the Guardian had a piece that used data from NASA to show how the air masses over the Northern Hemisphere have been disturbed by unusually warm air.
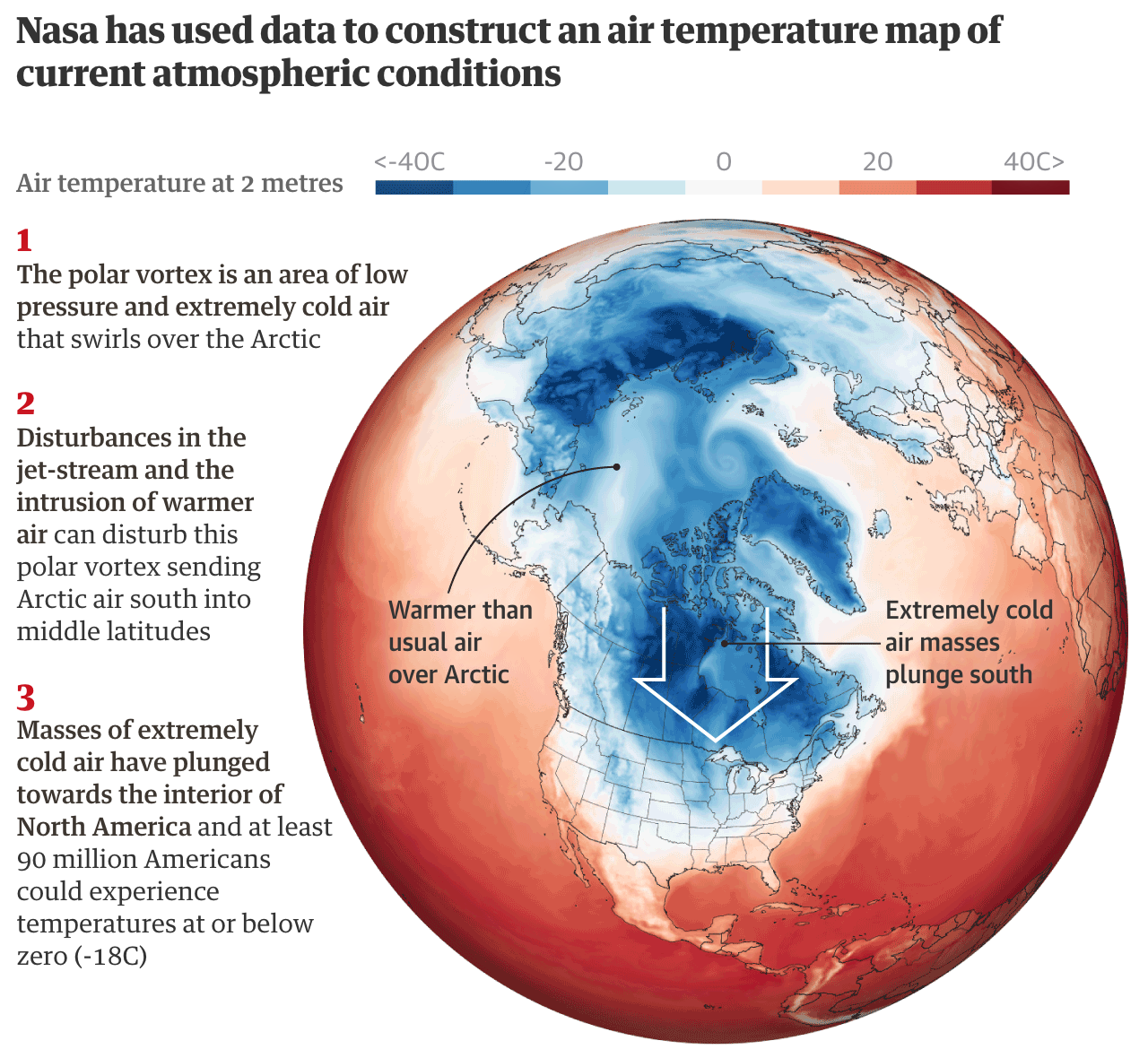
One theory to how this all works is that the reduced polar sea ice means water absorbs summer heat instead of being locked in the ice. But then that heat is basically released come winter. (I’m oversimplifying this.) That warms the air, which disturbs the polar vortex. As the Guardian then explains, the destabilised air mass can wobble and spill some of its frigid air down into the lower latitudes. (It takes a little while because the polar vortex is in the upper atmosphere and the air needs to sink to the ground.)
Point is, bundle up and stay warm.
Credit for the piece goes to the Guardian graphics department.