On 8 June, Britons will go to the polls in a general election that Prime Minister Theresa May called to increase her parliamentary majority. The United Kingdom faces a number of issues—I am looking at you housing and the NHS for starters—but Brexit is on the minds of a lot of people.
That makes sense, because if you recall the nation split 52–48 to leave the European Union last June. But, as the Financial Times explained the other day, that split is not as even as it used to be and that may have significant ramifications for the Conservative Party not to mention Labour and the Liberal Democrats.
The author explains the piece in nice detail, but this graphic including along with the article does a fantastic job showing the movements.
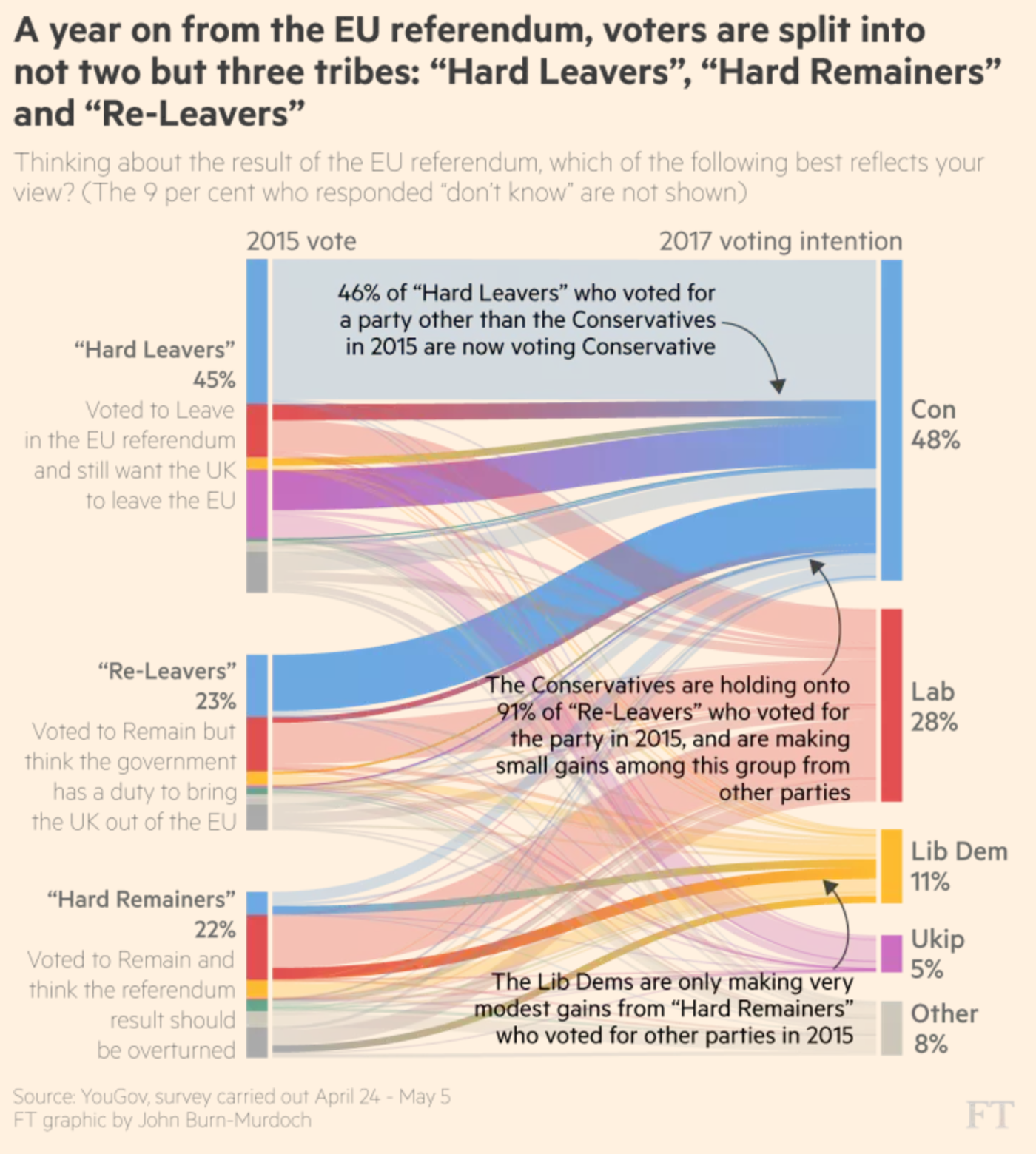
As you can probably guess, I am a huge fan of the annotations. Although I would argue that the centre and lower two, by being placed over the graphic, may be a bit illegible. But the concept is fantastic. It shows you just how difficult it will be for Labour and the Lib-Dems to beat May in June.
Credit for the piece goes to John Burn-Murdoch.