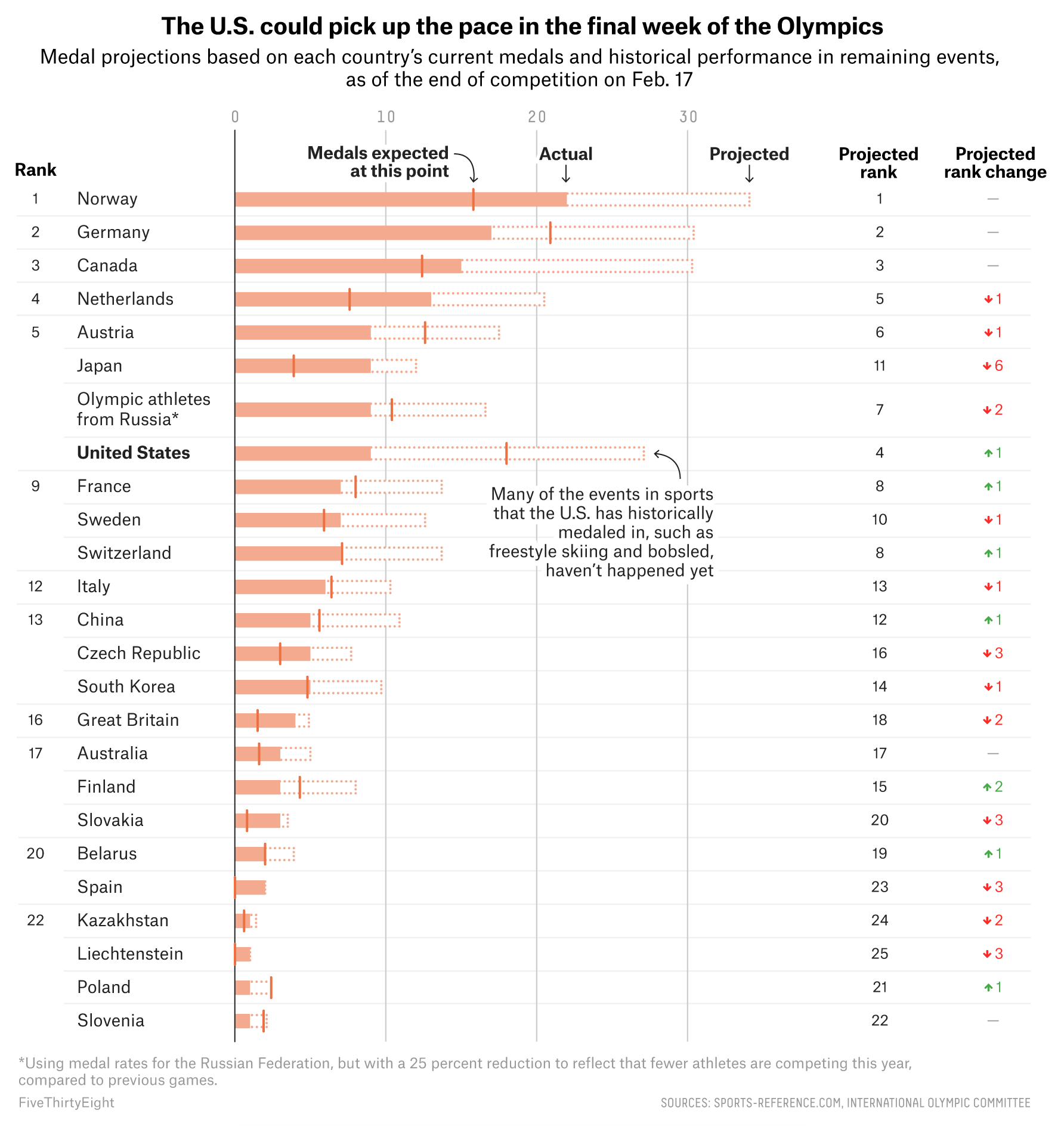
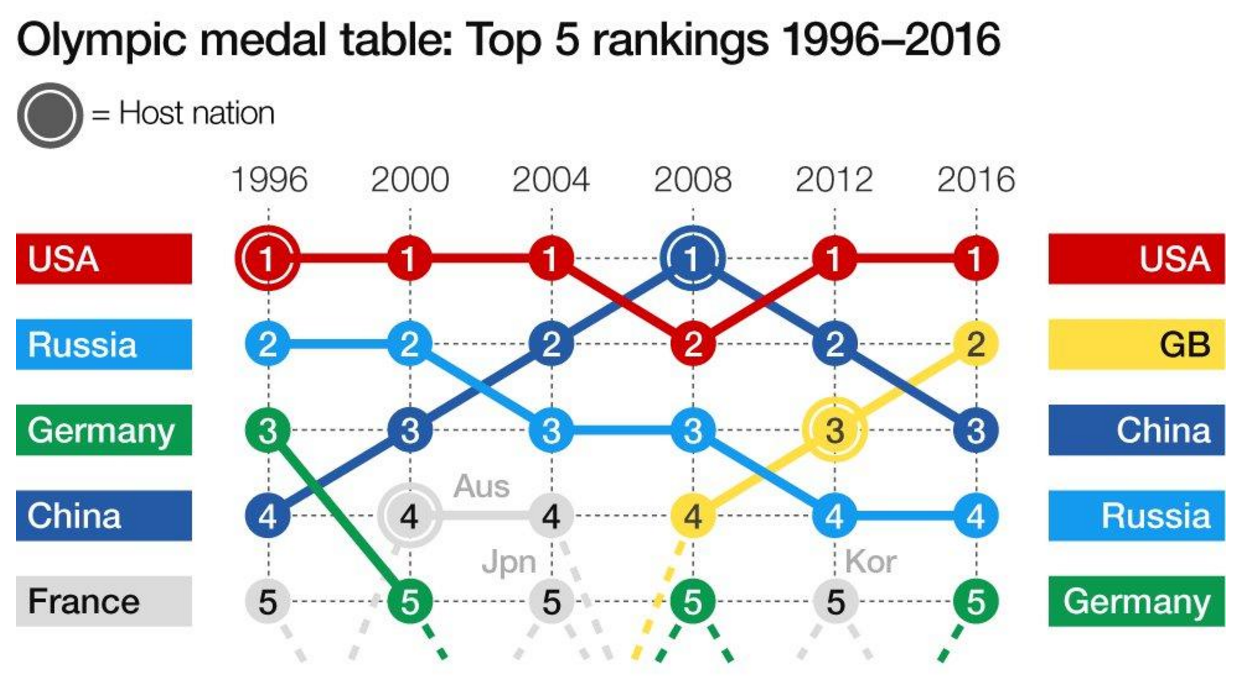
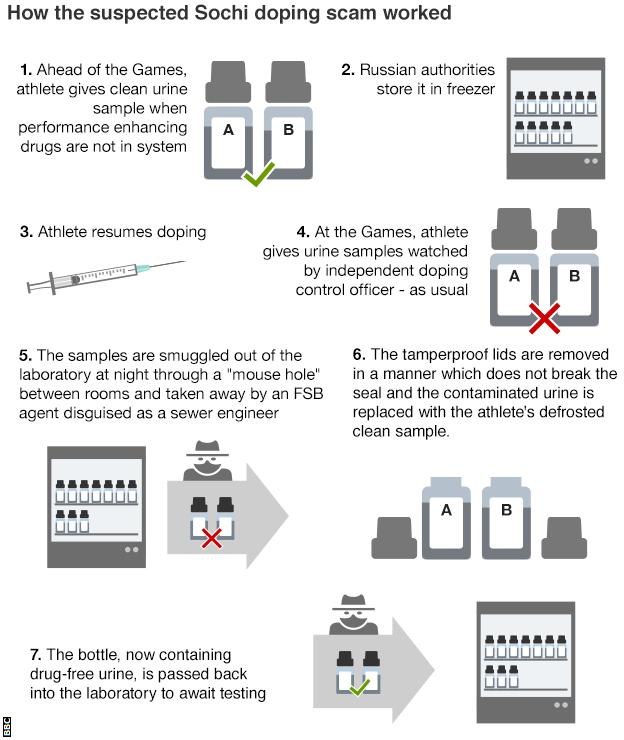
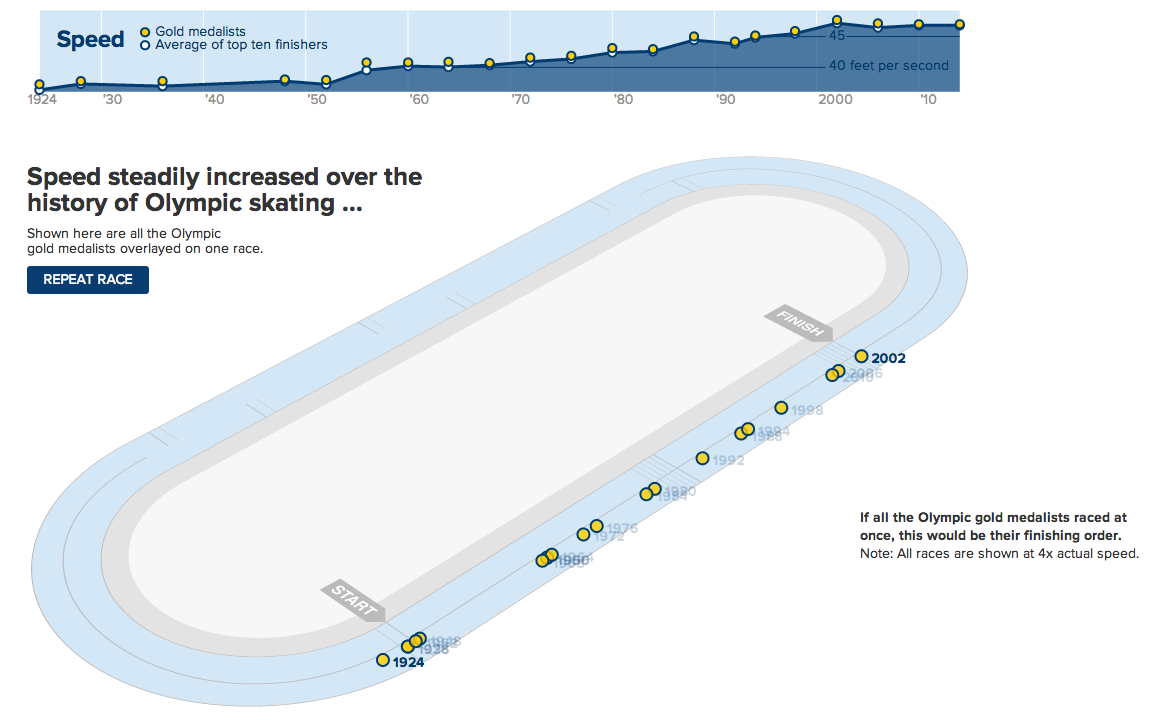
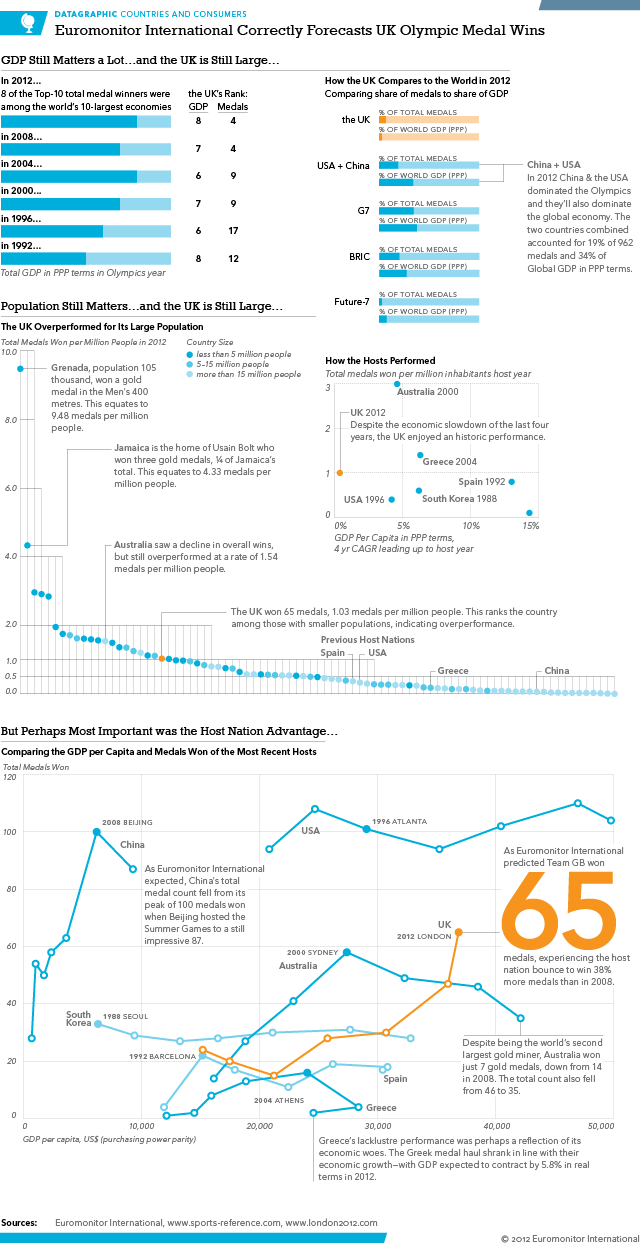
Every four years (or so) I have to confess that I think fondly back upon my former job, because I worked with a few wonderful colleagues of mine on some data about the Olympics. And the highlight was that we had a model to try and predict the number of medals won by the host country as we were curious about the idea of a host nation bump. In other words, do host countries witness an increase in their medal count relative to their performance in other Olympiads?
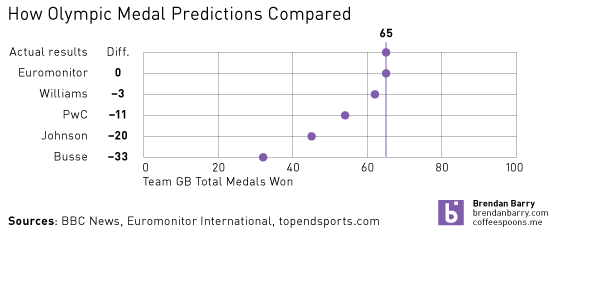
We concluded that host nations do see a slight bump in their total medal count and we then forecast that we expected Team GB (the team for Great Britain and Northern Ireland) to win a total of 65 medals. We reached 64 by the final day and it wasn’t until the women’s pentathlon when, in maybe the last event, Team GB won a silver medal bringing its total to 65, exactly in line with our forecast.
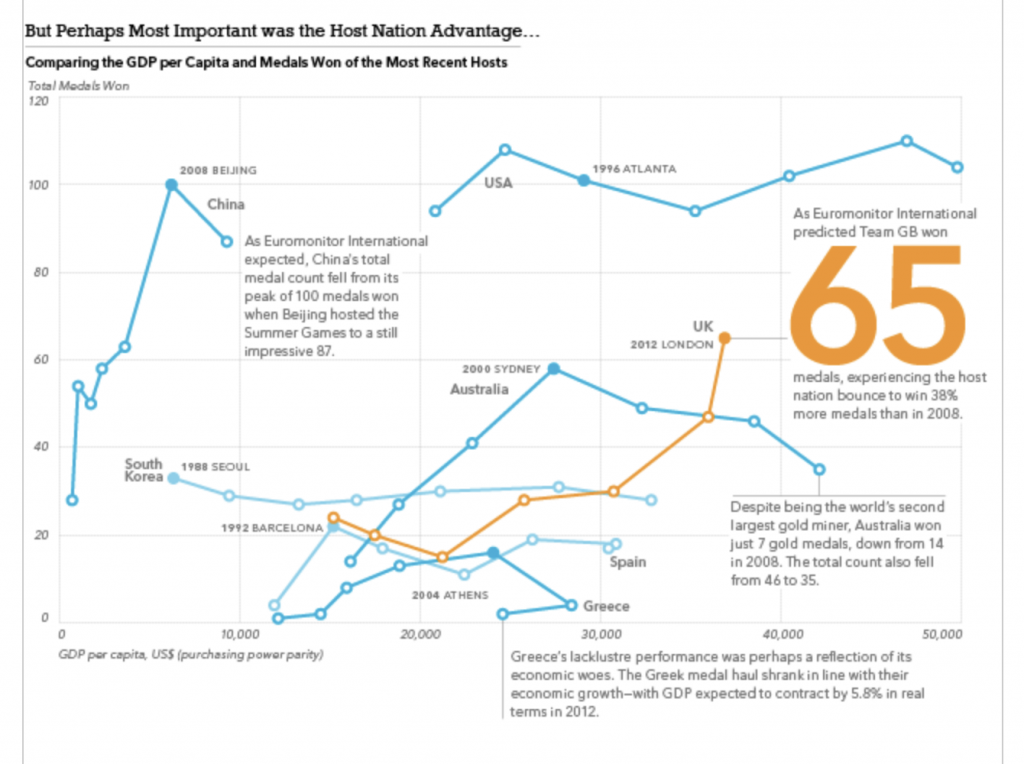
Of course we also looked at the data for a number of other things, including if GDP per capita correlated to Olympic performance. We also looked at BMI and that did yield some interesting tidbits. But at the end of the day it was the medal forecast that thrilled me in the summer of 2012.
So yeah, today’s a shameless plug for some old work of mine. But I’m still proud of it two olympiads later.
If you’d like to see some of the pieces, I have them in my portfolio.
Credit for the piece is mine.