Last month the US Census Bureau published their first batch of 2018 population estimates for states and counties. Pennsylvania is one of those states that is growing, but rather slowly. It will likely lose out to southern and western states in the 2020 census after which House seats will be reapportioned and electoral college votes subtracted.
From 2018 to 2010, the Commonwealth has grown 0.8%. Like I said, not a whole lot. But unlike some states (Illinois), it is at least growing. But Pennsylvania is a very diverse state. It has very rural agricultural communities and then also one of the densest and largest cities in the entire country with the whole lot in between . Where is the growth happening—or not—throughout the state? Fortunately we have county-level data to look at and here we go.
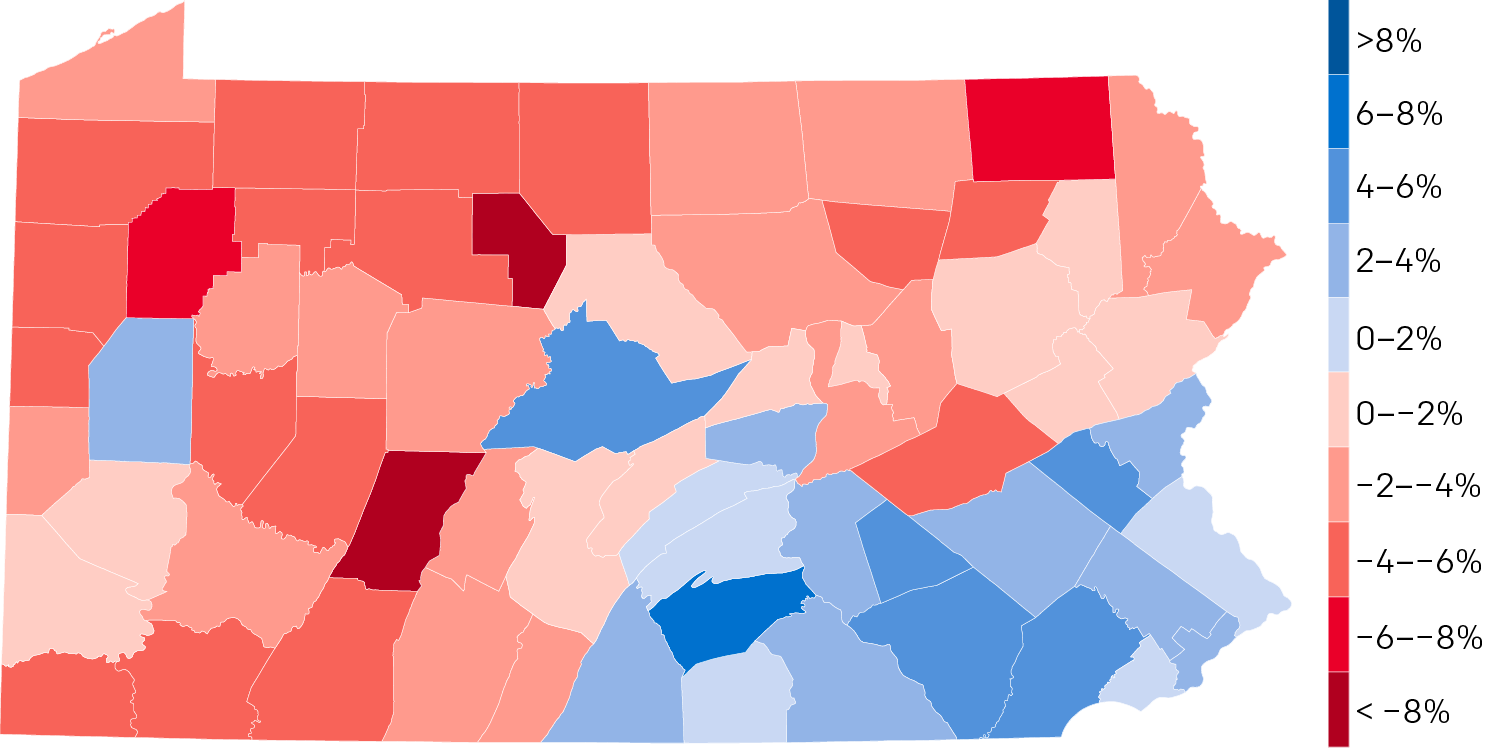
The most immediate takeaway is that the bulk of the growth is clearly happening in the southeastern part of the state, that is, broadly along the Keystone Corridor, the Amtrak line linking Harrisburg and Philadelphia. It’s also happening up north of Philadelphia into the exurbs and satellite cities.
We see two growth outliers. The one in the centre of the state is Centre County, home to the main campus of Pennsylvania State University. And then we have Butler County in the west, just north of Pittsburgh.
The lightest of reds are the lowest declines, in percentage terms. And those seem to be clustered around Scranton and Pittsburgh, along with the counties surrounding Centre County.
Everywhere else in the state is shrinking and by not insignificant amounts. Of course this data does not say where people are moving to from these counties. Nor does it say why. But come 2020, if the pattern holds, the state will need to take a look at its future planning. (Regional transit spending, I’m looking at you.)
